Theme: New Trends and Technologies in Stem Cell Research
STEMGEN 2019
STEMGEN 2019
12th Annual Conference on Stem Cell And Regenerative Medicine which is going to be held on June 13-14, 2019 in Helsinki, Finland provides a great opportunity to network with the world-class researchers in the fields of Stem Cells, Molecular Biology, Genetics, Medical Research, Biotechnology. This social gathering warmly welcomes Presidents, CEO's, Delegates and present-day experts from the field of Gene therapy and Public well-being and other pertinent organization positions to take an interest in these Keynote Talks, Sessions Talks and B2B networking. StemGen 2019 will also have a wide range of showcase of collaborators, exhibitors to explore. This global meeting gives the chance to Molecular Biologist, Gene & Cell Therapists, Young Researchers and students throughout the world to assemble and take in the most recent advances in the field of Stem Cell and Gene Therapy and to trade innovative thoughts and encounters.
Why attend???
With individuals from all around the globe concentrated on findings of Stem Cells and Gene Therapy and its advances; this is the best chance to achieve the largest gathering of members from the Stem Cell and Gene Therapy research groups. Lead introductions, circulate data, meet with present and potential researchers.
Who Should Attend?
-
Gene Therapy Scientists
-
Stem Cell Researchers
-
Emeritus and Academic professors
-
Cell Biologists
-
Genetic scientist
-
Molecular Biologists
-
Stem Cell research students
-
Business Entrepreneurs
-
Drug Manufacturing Companies
-
Stem cell Developers and Investigators
Track 1: Stem Cell Biology and Epigenetics
Stem Cells are those which are undifferentiated at the biological level and have an ability to divide to produce many stem cells. They can be found in multicellular living organisms. In mammals, there are two broad types of stem cells: Embryonic and Adult stem cells. Embryonic Stem cells are also known as pluripotent stem cells isolated from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, where Adult stem cells are found in various tissues. The main function of stem cells and progenitor cells is to act as a repair system for the body, replenishing adult tissue. Epigenetics is the study of changes in organisms caused by modification of gene expression rather than alteration of the genetic code itself. Epigenetic modifications are reversible modifications on a cell’s DNA that affect gene expression without altering the sequence of DNA. Epigenetic modifications play an important role in gene expression and regulation and are involved in numerous cellular processes such as in differentiation or development and tumorigenesis. Epigenetics is a study on a global level and through the adaptation of genomic high-throughput assays.
Track 2: Stem Cell Niches
The anatomical region where stem cells are found in a shallow recess is referred to a stem-cell niche. It refers to a microenvironment with reference to the in vivo or in vitro stem cells; they even interact with stem cells to regulate cell fate. Various niche factors act on embryonic stem cells to induce the cell proliferation and cell differentiation for the development of the fetus and in altering the gene expression during the embryonic development. In the human body, stem cells maintain the adult stem cells in a dormancy state, but during the tissue injury, it actively signals to stem cells to promote either self-renewal or differentiation to form new tissue.
Track 3: BioBanking and Tissue Preservation
Bioprocessing is a technology used for transferring the current laboratory-based practice of stem cell tissue culture to the clinical research as therapeutics necessitates for the application of engineering principles and practices to achieve control, automation, safety, validation and reproducibility of the process and the product. Biobanks are the type of biorepositories which collects, processes, stores and distributes biospecimens to support the future scientific investigation. This plays an important role in helping the researchers providing the background knowledge of the subject. In order to preserve tissues and stem cells collected for scientific purposes, a number of important techniques and protocols must be utilized. Moreover, the predominant methods in widespread use, cryopreservation, and hypothermic storage have shortcomings in application and assessment.
Track 4: Scaffolds and Tissue Regeneration
Scaffolds are of great importance in clinical medicine. It is an upcoming field and usually associated with conditions involving organ disease or failure. It is used to rebuild organs and return normal function. Stem cells along with regenerative medicine can be used to create ‘Scaffolds’ in the human body. Tissue regeneration is a branch of Regenerative medicine which deals with the study of regrowth or repair of the damaged or lost tissues in response to the injury. Non-injured tissues by default have expanded cells in the formation over time, but the new cells formed in response to the injury replaces the expanded cells in closing up the wounded site leaving a scar mark on the skin. For example, an injured cell is regenerated in 4-5 weeks, whereas a non-injured cell regenerates in just 3-4 days.
Track 5: Regenerative Medicine and Therapeutics
The process of “replacing tissues or organs, engineering or regenerating human cells to restore or establish normal function” is generally termed as Regenerative medicine. Regenerative medicine is a branch of Translational Research in the areas of tissue engineering and molecular biology. Regenerative medicine stimulates the body’s own repair mechanisms to engineer the damaged tissues and organs.
Track 6: 3D Bioprinting and Biofabrication
3D printing is a 3-dimensional printing machine which gives the information of a 2D image in the form of a 3D object. The layer of materials to form a 3D object is controlled by the computer by providing geometry of the object. 3D Bioprinting aids Tissue Engineering by providing in-depth information about the image and structure analysis of the image, which helps in solving the critical problems. Bio-fabrication is referred to as the production of artificial organs or tissues to address health challenges in medicine. It often uses the principle of 3D Bioprinting to form cells, gels, and fibers into an organ.
Track 7: Diseases and Stem Cell Treatment
Stem cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat/prevent disease. The bone-marrow transplant is the most widely used stem cell therapy, but some therapies derived from umbilical cord blood are also in use. Research is underway to develop various sources for stem cells, as well as to apply stem cell treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. The most well-established and widely used stem cell treatment is the transplantation of blood stem cells to treat diseases and conditions of the blood and immune system or to restore the blood system after treatments for specific cancers.
Track 8: Stem Cell Transplantation and Biomaterials
Stem cell transplantation also referred to as bone marrow transplant, in which unhealthy blood-forming cells replace with healthy cells. A procedure in which a patient receives healthy stem cells to replace their own cells destroyed by disease or high doses of anticancer drugs or by the radiation that are given as part of the procedure. The healthy stem cells may come from the bone marrow of the patient, blood, from a donor or from the umbilical cord blood. A stem cell transplant may be autologous, allogeneic or syngeneic. Many researchers are working to improve stem cell transplantation procedures to make it an option for patients.
Track 9: Stem Cell Apoptosis and Signal Transduction
Self-reestablishment and multiplication of foundational microorganism populaces are controlled, to some degree, by the affectation of apoptosis. Apoptosis of stem cells is a dynamic process which changes accordingly to the response to environmental conditions. The number of stem cells is always balanced between the lost through cell differentiation and to the gained through proliferation. Self-renewal and multiplication are controlled to some degree by the affectation of apoptosis. Because of natural conditions apoptosis of immature microorganisms is accepted to be dynamic.
Track 10: Cell and Organ Regeneration
It has been stated that stem cells have an ability to produce a large number of cells which in turn helps in forming the destroyed tissue or an organ. In contrast, stem cells can also be aided in repairing the damaged organs, in which the mechanism carries out in two different options: support mechanism and replace option. The support mechanism of the stem cell is regeneration or the regrowth of the tissue or organ cells avoiding detrimental fibrosis. The replace option of the stem cell is to transplant the stem cell.
Track 11: Ageing and Illness
Injury or sickness of individuals makes their cells to die or dysfunctional. Aging is the demonstration of the internal depletion of stem cells. It shows that human beings could not without stem cells. For a diverse group of treatment purpose, adult stem cells can be used. Adult Stem cell resides in-vivo in the form of self- renewing pools & helps in repairing/replacement of damaged tissues over the survival of the organism.
Track 12: Nano Therapies
Nanotechnology is the branch of technology that deals with small things that are less 100 nm in size. Here, to tackle the position of stem cells for some biotherapeutic applications we need to work at the size scales of molecules & processes that govern stem cells fate. Nanotechnology and Nanoscience offer immense benefits to humans with an effective amalgamation of nanotechnology & stem cells.
Track 13: Gene Therapy and Cell Therapy for Diseases
Gene Therapy is used to treat inherited Muscular disorder, cardiovascular disorder, HIV, cancer etc. In stem cell transplants, stem cells replace cells damaged by chemotherapy or disease or as a way for the donor's immune system to provoke immunity against some types of cancer and blood-related diseases, such as leukemia. Cell Therapy is internationally recognized for its novel approaches in treating blood-related disorders like leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma, and other life-threatening diseases. The stem cell transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCT) in which the allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells are harvested from healthy donors of same species and autologous stem cell from the patient itself. Both therapies use high dosage cytotoxic medication in order to induce higher remission rates against malignant diseases. Autologous HSCT preferably used in relapsed malignant high-grade lymphoma and Allogeneic HSCT preferred for therapeutic effect against acute leukemia with unfavorable prognosis in a high percentage of patients. The Recent developments based on the expansion of the donor pool for allogeneic stem cells in order to reduce dosage as well as the chemotherapeutic toxicity of allogeneic transplantation with sustainable anti-leukemia efficacy.
Track 14: Viral Gene Therapies
Classical methods of gene therapy include transfection. It became inefficient and limited mainly due to the delivery of the gene into actively proliferating cell s in-vitro. Gene therapy utilizes the delivery of DNA into cells by means of vectors such as biological in-vitro or viral vectors and non-viral methods. Several kinds of viruses vectors used in gene therapy are the retrovirus, adeno-associated virus, and herpes simplex virus. While other recombinant viral vector systems have been developed, retroviral vectors remain the most popular vector system for gene therapy protocols and widest application due to their historical significance as the first vectors developed for efficient gene therapy application and the infancy of the field of gene therapy.
Track 15: Genome Editing Technology
Genome editing technology deals with engineered nucleases and it is the emerging type of genetic engineering. It is the technology in which the DNA is inserted, deleted or replaced in the genome. The emergence of highly versatile genome-editing technologies has provided investigators with the ability to rapidly and economically introduce sequence-specific modifications into the genomes of a broad spectrum of cell types and organisms. It also promotes various changes in subcellular level genome editing itself also holds tremendous potential for treating the underlying various idiopathic genetic causes of certain diseases. The core technologies now most commonly used techniques to facilitate genome editing are clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs), zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs), and homing endonucleases or mega-nucleases.
Track 16: Bioengineering Therapeutics
Tissue engineering is the combinational usage of cells, engineering, materials methods, suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors in order to improve or replace the infected biological tissues. The field includes the development of materials, devices, techniques to detect and differentiate disease states, the treatment response, aid tissue healing, precisely deliver treatments to tissues or cells, signal early changes in health status, and provide implantable bioartificial replacement organs for recover or establish of healthy tissue. Techniques developed here identify and detect biomarkers of disease sub-types, progression, and treatment response, from tissue imaging, gene testing and gene analysis, that aid the more rapid development of new treatments and guide their clinical applications in treating the disorder. It includes the usage of computational modeling, bioinformatics, and quantitative pharmacology to integrate data from diverse experimental and clinical sources to discover new drugs and specific drug targets, as well as to design more efficient and informative preclinical, clinical safety and efficacy studies.
Track 17: Advanced Gene Therapeutics
Therapeutics is the branch of science dealing with the application of remedies of diseases. Moving on to the gene therapeutics it is the medicine which we develop a remedy for disease through the genetic material. Advanced gene therapeutics is a medicine we use the drugs to treat a disease by developing dosage forms to optimize drug action, underpin new formulations that target molecules spatially within the body, enhance the bioequivalence of poorly soluble drugs and biologics, and improve patient experience and compliance.
Track 18: Disease Modeling and Drug Discovery
Infectious diseases remain a leading cause of deaths globally. Scientific models are utilized to comprehend the transmission of infections. The applications incorporate deciding ideal control approaches against new or treating infections, such as swine flu, Ebola, HIV, Zika, malaria, and tuberculosis. It can be used to predict the impact of vaccination strategies against common infections such as rubella and measles. The process of research or discovery of a medicine for a disease is generally called as drug discovery. In contrast, patient-specific drug discovery is a process of inventing a drug by considering the pros and cons and the anatomical conditions of the patient. The general medicine is discovered on the basis of the active ingredient from traditional remedies or serendipitous discovery. It can also be referred to as personalized medicine, which separates patients into different categories.
Track 19: Ethical Issues of Gene Therapy
The world trade market for cell and gene therapies is expected to greater than the $20 billion USD mark by 2025, with an annual growth rate of 21%. The main targets for cell-based therapies are high impact disease areas with significant incurable needs, including cancer, heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases, musculoskeletal disorders and autoimmune diseases gene therapies should then not be rushed to market but companies should gather the required data about the impact of therapy in human community with the appropriate duration of follow-up to allow proper evaluation by payers.
Track 20: Clinical Trials on Stem Cell & Gene Therapy
Clinical trials on gene therapy products are often varying from the clinical trials design for other types of pharmaceutical products. The differences in trial design are necessitated by the distinctive features of these products. The clinical trials also reflect previous clinical experience and evidence of medicine. Early experiences with products indicate that some Gene Therapy products may pose substantial risks to subjects due to the effect at the cellular and genetic level. The design of early-phase clinical trials of Gene therapy products often involves the following consideration of clinical safety issues, preclinical issues, and chemistry, manufacturing and controls (CMC) issues that are encountered.
STEMGEN 2019
Market Analysis
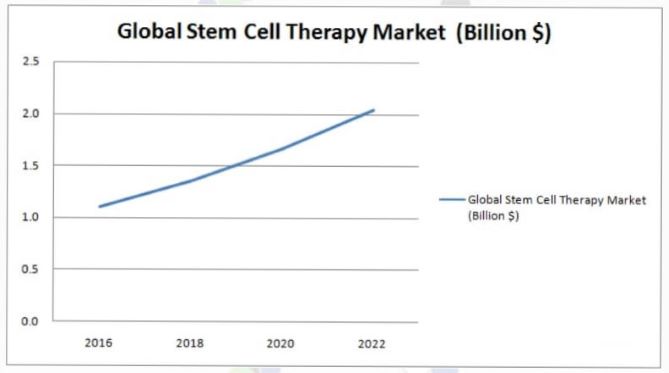
Stem cell therapy Market is expected to reach USD 145 million by 2021, growing at a CAGR of 11.0% during the forecast period. Factors such as the growing awareness related to the therapeutic potential of stem cell disease management, development of advanced genome based cell analysis techniques, increasing public-private investments in infrastructure for stem cell banking and processing are propelling the growth of the global stem cell therapy market.
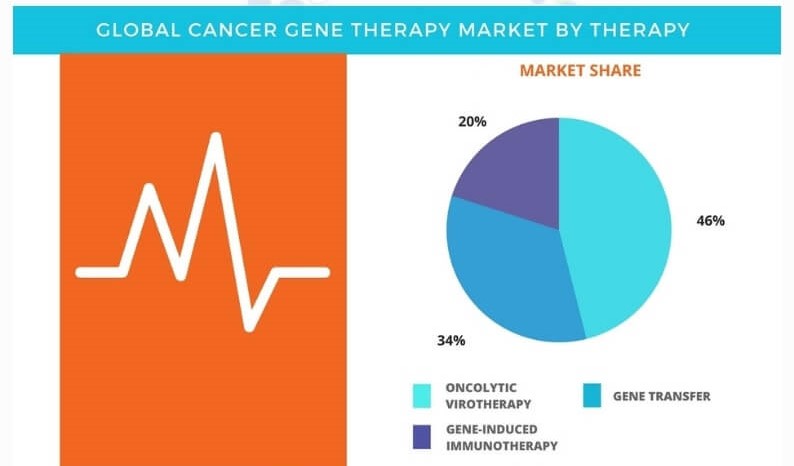
The rising prevalence rate of cancer has been a huge challenge for global economics as the disease leads to a high rate of mortality and economic losses. The current treatment options available come with many drawbacks such as severe side effects and relapse of cancer. These factors have led to high investment in the R&D for the development of various novel therapies with cancer gene therapy being one of the major ones of them. The therapy mainly uses three types of treatment options namely oncolytic virotherapy, gene transfer therapy, and gene-induced immunotherapy.
The global gene therapy market size was valued at USD 7.6 million in 2017. it is estimated to expand at CAGR of over 19.0% during the forecast period. Increasing the number of molecules in the development phase is expected to stroke market growth.
Why Helsinki
Helsinki is the Capital of Finland. Scientists in Finland are working on making stem cells as key to youth. Stem cell research is widely recognized and funded in European Countries where researchers doing great work on stem cell and regenerative medicine. In fact, ensuring the principle that stem cell research provides a vast perspective to create new treatments for several serious diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
The location of the Helsinki Airport is the neighboring city of Vantaa, which has frequent service to many destinations in Europe and Asia. Helsinki was the World Design Capital of 2012.
Conference Highlights
- Stem Cell Biology and Epigenetics
- Stem Cell Niches
- Bio Banking & Tissue Preservation
- 3D Bioprinting & Biofabrication
- Clinical Trials on Stem Cell & Gene Therapy
- Diseases and Stem Cell Treatment
- Scaffolds and Tissue Regeneration
- Regenerative Medicine and Therapeutics
- Disease Modelling and Drug Discovery
- Stem Cell Transplantation and Biomaterials
- Ageing and Illness
- Stem Cell Apoptosis and Signal Transduction
- Cell and Organ Regeneration
- Nanotherapy
- Gene Therapy and Cell Therapy for Diseases
- Viral Gene Therapies
- Genome Editing Technology
- Bioengineering Therapeutics
- Advanced Gene Therapeutics
- Ethical Issues of Gene Therapy
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 13-14, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Stem Cell Research & Therapy
- Journal of Genetic Syndromes & Gene Therapy
- Journal of Transplantation Technologies & Research
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by




